Your system of record and your system of intelligence is the same.
In today’s AI-driven world, enterprises need more than just fast queries or scalable storage, they need a unified data foundation that can power both real-time transactional workloads and vector-based AI applications. Traditionally, these two worlds have lived apart: transactional databases handled the operational data, while vector stores powered AI search and semantic similarity. But that separation comes at a cost: data fragmentation, slow pipelines, and operational complexity.
What if you could have both in one system? That’s exactly what CockroachDB delivers: a distributed SQL database that scales globally and now brings pgvector-compatible native vector capabilities into the same platform. The result? A single PostgreSQL-compatible database that performs at scale for both transactional and vector data — the perfect foundation for today’s AI-powered enterprises.
The Enterprise AI Challenge
AI applications, especially those that leverage large language models (LLMs) and real-time personalization, demand more from their data infrastructure than ever before. Enterprises must:
Combine structured operational data (users, products, orders, etc.) with unstructured or semi-structured embeddings.
Build for production not pilots and scale to not millions but billions of vectors.
Serve real-time responses while maintaining strong consistency and security.
Scale globally without downtime or complex replication setups.
Optimize for both cost and performance, without managing multiple specialized data systems.
Most companies today patch together multiple tools: a relational database for transactions, a vector store for embeddings, and custom CDC pipelines to sync the two. This creates latency, fragility, and maintenance overhead, especially at enterprise scale.
The CockroachDB Advantage: One System for Both Worlds
CockroachDB’s distributed SQL architecture brings together strong consistency, horizontal scalability, and cloud-native resilience. Adding vector support means it can now handle the new class of AI workloads directly. There’s no need to ship data elsewhere for embedding searches or context retrieval.
Along with CockroachDB’s distributed vector indexing, purpose-built to provide fresh, low-latency index results, you can build a system that manages your core data. Enterprises can:
Store vectors alongside traditional relational data.
Perform hybrid queries that mix structured filters with vector similarity search.
Keep embeddings fresh in real-time; no lag, no synchronization delays.
Maintain global consistency and uptime, even across multiple regions.
In other words, CockroachDB is both your system of record and your system of intelligence.
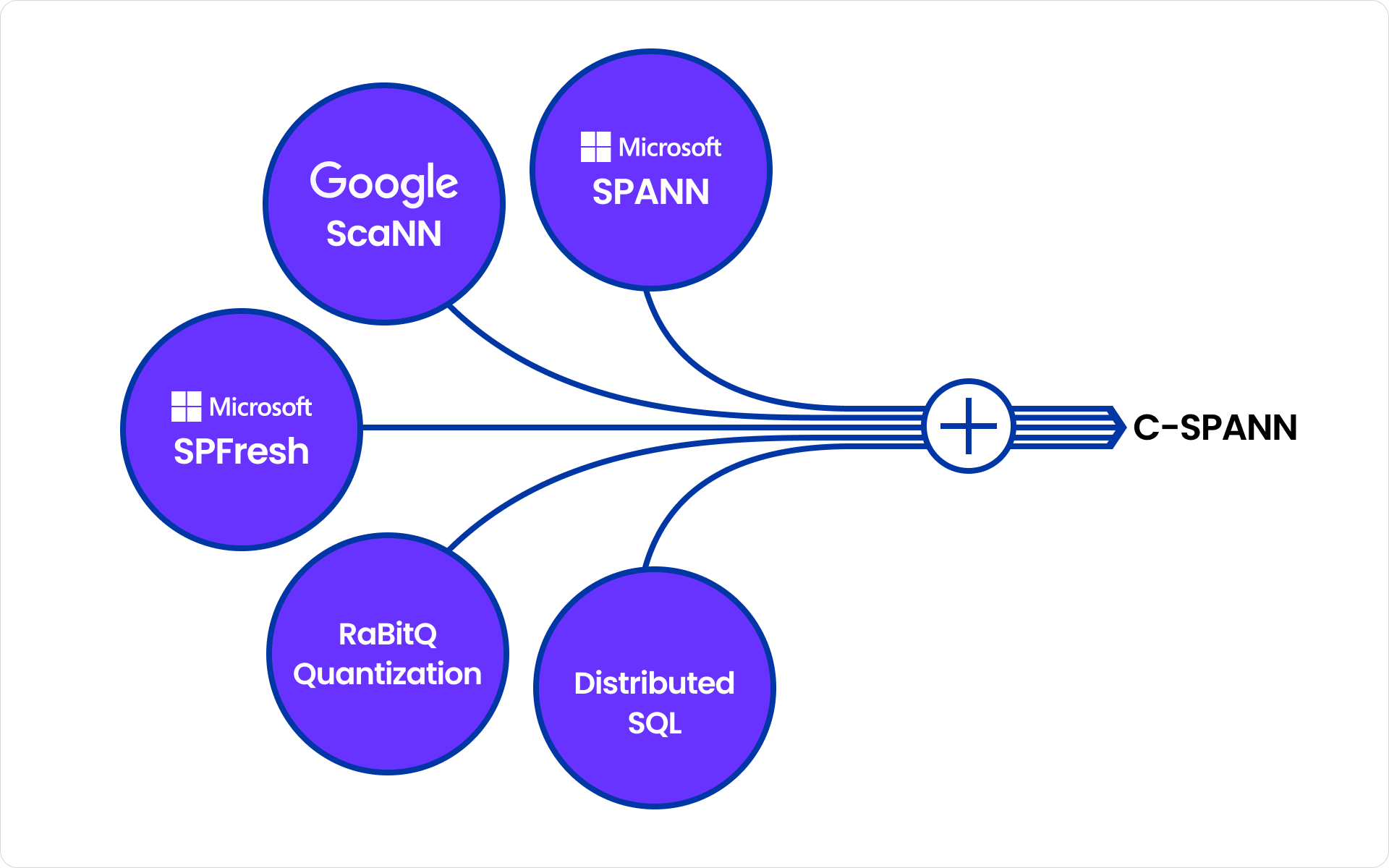
Currently, CockroachDB is pioneering a new frontier in real-time vector indexing through its C-SPANN architecture, which integrates vector search directly into its distributed SQL engine to support semantic and embedding-based workloads at global scale. Unlike traditional vector systems that rely on static, single-node indexes or batch updates, our approach supports continuous inserts and deletes, automatic rebalancing, and distributed execution across regions, ensuring fresh and consistent search results without specialized infrastructure.
C-SPANN achieves low-latency retrieval for billions of vectors by using a hierarchical K-means partition tree and a novel quantization method called RaBitQ, which compresses data by about 94 percent while maintaining accuracy through a two-stage search and rerank process. This innovation matters because modern AI applications require live, transactional, and intelligent data systems that can combine structured and unstructured information in real time. By unifying vector search with transactional data in one resilient, globally distributed platform, CockroachDB eliminates data silos and enables enterprises to build truly intelligent, responsive, and scalable AI-powered systems.
Real-Time Agentic Systems, Powered by Your Data
The future of enterprise AI is agentic: autonomous systems that reason, decide, and act in real time using live business data. Building these systems requires three key ingredients:
Real-time access to transactional context (e.g., who the user is, what they’re doing).
Semantic understanding of unstructured data (e.g., documents, chats, logs).
Scalable, consistent infrastructure to tie it all together.
CockroachDB makes this possible by bringing both data types — structured and vector — into a single, high-performance platform. Developers can now build real-time agentic applications that:
Generate and retrieve relevant context instantly.
Adapt to live data updates without retraining or manual syncing.
Scale globally while preserving performance and cost efficiency.
Performance, Cost, and Scale — Without Compromise
Unlike specialized vector databases that sacrifice consistency or transactional integrity for speed, CockroachDB delivers all three:
Performance: Distributed query execution and low-latency vector search.
Cost-efficiency: A unified stack means fewer moving parts and lower ops overhead.
Scale: Proven architecture that scales elastically across clouds and regions.
This unified approach is not just about convenience, it’s about enabling a new generation of enterprise-grade AI applications that are both intelligent and trustworthy.
The Future Is Unified
AI is no longer an add-on; it’s a fundamental part of how enterprises operate. The infrastructure behind it must evolve accordingly. By bringing vectors into distributed SQL, CockroachDB has created the ideal platform for the modern AI stack, one where real-time data, intelligence, and scale all live together.
Microsoft Ignite with Cockroach Labs (November 20)
With CockroachDB, enterprises can finally build and deploy AI systems that are fast, consistent, and global by design without sacrificing control or simplicity. Want to learn more? Come join our session at Microsoft Ignite where we talk about how to build the next generation of AI systems.
David Joy is a Senior Manager of Sales Engineering at Cockroach Labs and the host of the podcast, Big Ideas in App Architecture.