
This page shows you how to reproduce CockroachDB TPC-C performance benchmarking results. Across all scales, CockroachDB can process tpmC (new order transactions per minute) at near maximum efficiency. Start by choosing the scale you're interested in:
| Workload | Cluster size | Warehouses | Data size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local | 3 nodes on your laptop | 10 | 2 GB |
| Local (multi-region) | 9 in-memory nodes on your laptop using cockroach demo |
10 | 2 GB |
| Small | 3 nodes on c5d.4xlarge machines |
2500 | 200 GB |
| Medium | 15 nodes on c5d.4xlarge machines |
13,000 | 1.04 TB |
| Large | 81 nodes on c5d.9xlarge machines |
140,000 | 11.2 TB |
Before you begin
Review TPC-C concepts
TPC-C provides the most realistic and objective measure for OLTP performance at various scale factors. Before you get started, consider reviewing what TPC-C is and how it is measured.
Request a trial license
Reproducing these TPC-C results involves using CockroachDB's partitioning feature to ensure replicas for any given section of data are located on the same nodes that will be queried by the load generator for that section of data. Partitioning helps distribute the workload evenly across the cluster.
The partitioning feature requires an Enterprise license, so request a 30-day trial license before you get started.
You should receive your trial license via email within a few minutes. You'll enable your license once your cluster is up-and-running.
Step 1. Set up the environment
Provision VMs
Create 86 VM instances, 81 for CockroachDB nodes and 5 for the TPC-C workload.
- Create all instances in the same region and the same security group.
- Use the
c5d.9xlargemachine type. - Use local SSD instance store volumes. Local SSDs are low latency disks attached to each VM, which maximizes performance. This configuration best resembles what a bare metal deployment would look like, with machines directly connected to one physical disk each. We do not recommend using network-attached block storage.
Note the internal IP address of each instance. You'll need these addresses when starting the CockroachDB nodes.
This configuration is intended for performance benchmarking only. For production deployments, there are other important considerations, such as security, load balancing, and data location techniques to minimize network latency. For more details, see the Production Checklist.
Configure your network
CockroachDB requires TCP communication on two ports:
26257for inter-node communication (i.e., working as a cluster) and for the TPC-C workload to connect to nodes8080for exposing your DB Console
Create inbound rules for your security group:
Inter-node and TPCC-to-node communication
| Field | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Custom TCP Rule |
| Protocol | TCP |
| Port Range | 26257 |
| Source | The name of your security group (e.g., sg-07ab277a) |
DB Console
| Field | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Custom TCP Rule |
| Protocol | TCP |
| Port Range | 8080 |
| Source | Your network's IP ranges |
Step 2. Start CockroachDB
The --insecure flag used in this tutorial is intended for non-production testing only. To run CockroachDB in production, use a secure cluster instead.
SSH to the first VM where you want to run a CockroachDB node.
Start CockroachDB using the
cockroach startcommand:cockroach start \ --insecure \ --advertise-addr=<node1 internal address> \ --join=<node1 internal address>,<node2 internal address>,<node3 internal address> \ --cache=.25 \ --locality=rack=0Each node will start with a locality that includes an artificial "rack number" (e.g.,
--locality=rack=0). Use 81 racks for 81 nodes so that 1 node will be assigned to each rack.Repeat these steps for the other 80 VMs for CockroachDB nodes. Each time, be sure to:
- Adjust the
--advertise-addrflag. - Set the
--localityflag to the appropriate "rack number".
- Adjust the
On any of the VMs with the
cockroachbinary, run the one-timecockroach initcommand to join the first nodes into a cluster:cockroach init --insecure --host=<address of any node on --join list>
Step 3. Configure the cluster
You'll be importing a large TPC-C data set. To speed that up, you can temporarily disable replication and tweak some cluster settings. You'll also need to enable the Enterprise license you requested earlier.
SSH to any VM with the
cockroachbinary.Launch the built-in SQL shell:
$ cockroach sql --insecure --host=<address of any node>Adjust some cluster settings:
SET CLUSTER SETTING kv.dist_sender.concurrency_limit = 2016; SET CLUSTER SETTING kv.snapshot_rebalance.max_rate = '256 MiB'; SET CLUSTER SETTING sql.stats.automatic_collection.enabled = false; SET CLUSTER SETTING schemachanger.backfiller.max_buffer_size = '5 GiB'; SET CLUSTER SETTING rocksdb.min_wal_sync_interval = '500us'; SET CLUSTER SETTING kv.range_merge.queue_enabled = falseChange the default GC TTL to the following value:
ALTER RANGE default CONFIGURE ZONE USING gc.ttlseconds = 600;Enable the trial license you requested earlier:
> SET CLUSTER SETTING cluster.organization = '<your organization>';> SET CLUSTER SETTING enterprise.license = '<your license key>';Exit the SQL shell:
> \q
Step 4. Import the TPC-C dataset
CockroachDB comes with a number of built-in workloads for simulating client traffic. This step features CockroachDB's version of the TPC-C workload.
SSH to the VM where you want to run TPC-C.
Import the TPC-C dataset:
$ cockroach workload fixtures import tpcc \ --partitions=81 \ --warehouses=140000 \ --replicate-static-columns \ --partition-strategy=leases \ 'postgres://root@<address of any CockroachDB node>:26257?sslmode=disable'This will load 11.2 TB of data for 140,000 "warehouses". This can take up to 8 hours to complete.
You can monitor progress on the Jobs screen of the DB Console. Open the DB Console by pointing a browser to the address in the
adminfield in the standard output of any node on startup.
Step 5. Partition the database
Partition your database to divide all of the TPC-C tables and indexes into 81 partitions, one per rack, and then use zone configurations to pin those partitions to a particular rack.
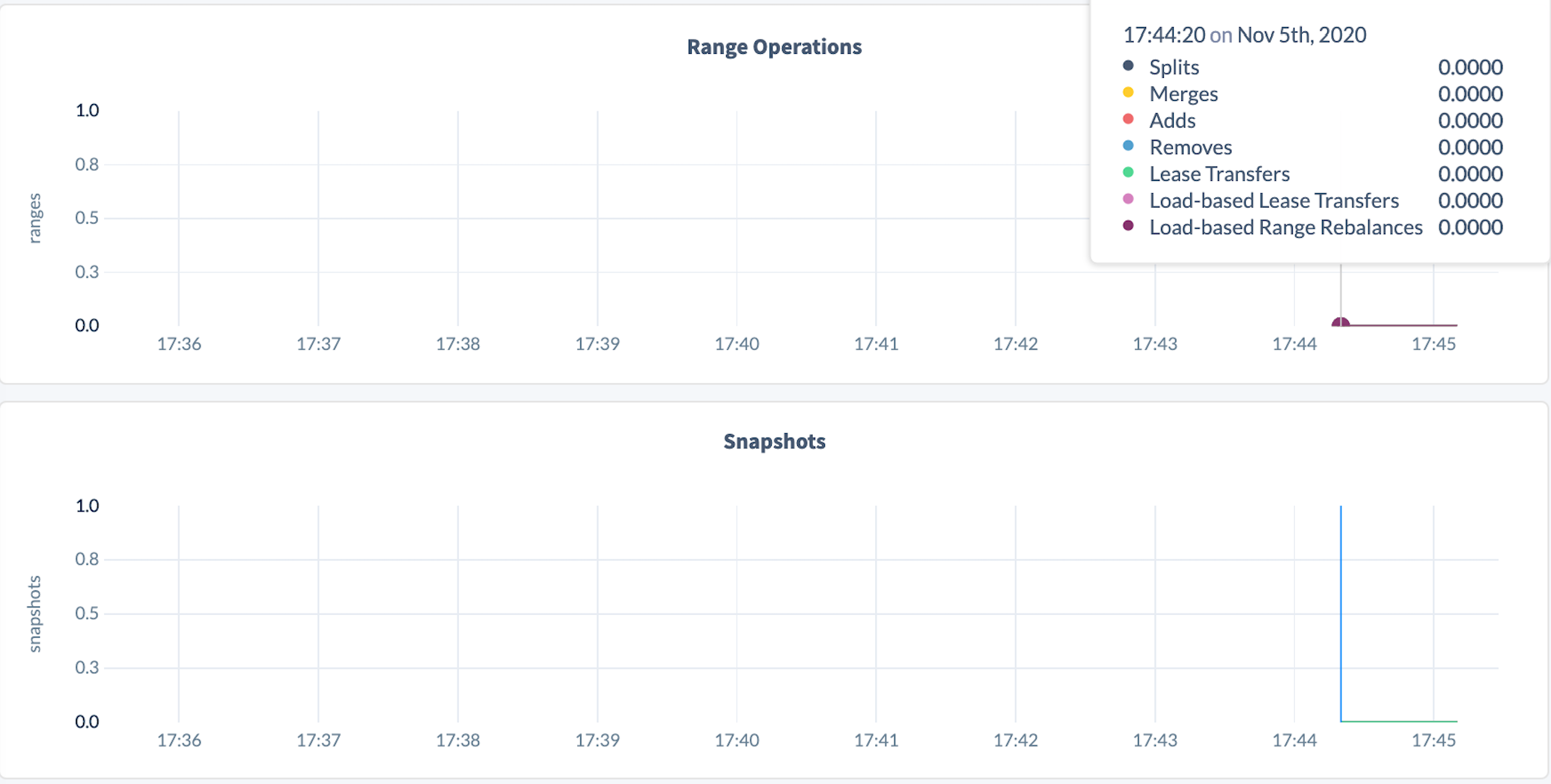
Wait for up-replication and partitioning to finish. You will know when they have finished because both the number of lease transfers and snapshots will go down to
0and stay there. This will likely take 10s of minutes.- To monitor the number of lease transfers, open the DB Console, select the Replication dashboard, hover over the Range Operations graph, and check the Lease Transfers data point.
- To check the number of snapshots, open the DB Console, select the Replication dashboard, and hover over the Snapshots graph.
Step 7. Allocate partitions
Before running the benchmark, it's important to allocate partitions to workload binaries properly to ensure that the cluster is balanced.
Create an
addrsfile containing connection strings to all 81 CockroachDB nodes:postgres://root@<node 1 internal address>:26257?sslmode=disable postgres://root@<node 2 internal address>:26257?sslmode=disable postgres://root@<node 3 internal address>:26257?sslmode=disable postgres://root@<node 4 internal address>:26257?sslmode=disable ...Upload the
addrsfile to the 5 VMs with theworkloadbinary:$ scp addrs <username>@<workload instance 1 address>:.$ scp addrs <username>@<workload instance 2 address>:.$ scp addrs <username>@<workload instance 3 address>:.$ scp addrs <username>@<workload instance 4 address>:.$ scp addrs <username>@<workload instance 5 address>:.SSH to each VM with
workloadand allocate partitions:ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc --partitions=81 \ --warehouses=140000 \ --partition-affinity=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 \ --ramp=30m \ --duration=1ms \ --histograms=workload1.histogram.ndjson \ $(cat addrs)ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \ --partitions 81 \ --warehouses 140000 \ --partition-affinity=17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32 \ --ramp=30m \ --duration=1ms \ --histograms=workload2.histogram.ndjson \ $(cat addrs)ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \ --partitions=81 \ --warehouses=140000 \ --partition-affinity=33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48 \ --ramp=30m \ --duration=1ms \ --histograms=workload3.histogram.ndjson \ $(cat addrs)ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \ --partitions=81 \ --warehouses=140000 \ --partition-affinity=49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64 \ --ramp=30m \ --duration=1ms \ --histograms=workload4.histogram.ndjson \ $(cat addrs)ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \ --partitions=81 \ --warehouses=140000 \ --partition-affinity=65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80 \ --ramp=30m \ --duration=1ms \ --histograms=workload5.histogram.ndjson \ $(cat addrs)
Step 8. Run the benchmark
Once the allocations finish, run TPC-C for 30 minutes on each VM with workload:
It is critical to run the benchmark from the workload nodes in parallel, so start them as simultaneously as possible.
ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \
--partitions=81 \
--warehouses=140000 \
--partition-affinity=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16 \
--ramp=4m \
--duration=30m \
--histograms=workload1.histogram.ndjson \
$(cat addrs)
ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \
--partitions=81 \
--warehouses=140000 \
--partition-affinity=17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32 \
--ramp=4m \
--duration=30m \
--histograms=workload2.histogram.ndjson \
$(cat addrs)
ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \
--partitions=81 \
--warehouses=140000 \
--partition-affinity=33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48 \
--ramp=4m \
--duration=30m \
--histograms=workload3.histogram.ndjson \
$(cat addrs)
ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \
--partitions=81 \
--warehouses=140000 \
--partition-affinity=49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64 \
--ramp=4m \
--duration=30m \
--histograms=workload4.histogram.ndjson \
$(cat addrs)
ulimit -n 500000 && cockroach workload run tpcc \
--partition=81 \
--warehouses=140000 \
--partition-affinity=65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80 \
--ramp=4m \
--duration=30m \
--histograms=workload5.histogram.ndjson \
$(cat addrs)
Step 9. Interpret the results
Collect the result files from each VM with
workload:$ scp <username>@<workload instance 1 address>:workload1.histogram.ndjson .$ scp <username>@<workload instance 2 address>:workload2.histogram.ndjson .$ scp <username>@<workload instance 3 address>:workload3.histogram.ndjson .$ scp <username>@<workload instance 4 address>:workload4.histogram.ndjson .$ scp <username>@<workload instance 5 address>:workload5.histogram.ndjson .Upload the result files to one of the VMs with the
workloadbinary:Note:The following commands assume you're uploading to the VM with the
workload1.histogram.ndjsonfile.$ scp workload2.histogram.ndjson <username>@<workload instance 2 address>:.$ scp workload3.histogram.ndjson <username>@<workload instance 3 address>:.$ scp workload4.histogram.ndjson <username>@<workload instance 4 address>:.$ scp workload5.histogram.ndjson <username>@<workload instance 5 address>:.SSH to the VM where you uploaded the results files.
Run the
workload debug tpcc-merge-resultscommand to synthesize the results:cockroach workload debug tpcc-merge-results \ --warehouses=140000 \ workload*.histogram.ndjsonYou'll should see results similar to the following, with 1.68M tpmC with 140,000 warehouses, resulting in an efficiency score of 95%:
Duration: 30m1., Warehouses: 140000, Efficiency: 95.45, tpmC: 1684437.21 _elapsed___ops/sec(cum)__p50(ms)__p90(ms)__p95(ms)__p99(ms)_pMax(ms) 1801.1s 2824.0 302.0 1140.9 2415.9 9126.8 55834.6 delivery 1801.1s 28074.0 402.7 1409.3 2684.4 9126.8 45097.2 newOrder 1801.1s 2826.0 6.8 62.9 125.8 4160.7 33286.0 orderStatus 1801.1s 28237.4 251.7 1006.6 2415.9 15032.4 103079.2 payment 1801.1s 2823.5 39.8 469.8 906.0 5905.6 38654.7 stockLevel
See also
Hardware
CockroachDB works well on commodity hardware in public cloud, private cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments. For hardware recommendations, see our Production Checklist.
Performance tuning
For guidance on tuning a real workload's performance, see SQL Best Practices, and for guidance on techniques to minimize network latency in multi-region or global clusters, see Multi-Region Capabilities Overview.